Key Takeaways
- Match the derivative to your goal: Use L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA) for fast, high-impact brightening and collagen support, and choose SAP, MAP, or AG when stability, gentleness, and long-term performance are the priority.
- Let format and skin concern drive selection:
- Serums: L-AA for robust skin; SAP/AG for sensitive or acne-prone.
- Creams/lotions: MAP or AG for anti-aging and brightening.
- Masks/wash-offs: SAP or MAP for short-contact, intensive treatments.
- Engineer for stability and efficacy: Control pH, use protective packaging plus antioxidant/chelating systems, and consider encapsulation or advanced delivery to preserve potency and optimize skin delivery.
- Validate and de-risk at scale: Back formulas with stability testing, lab/clinical data, and strong regulatory documentation, supported by reputable suppliers who ensure consistent quality and technical guidance.
- Leverage Vivify as a partner: Vivify Beauty Care’s portfolio of vitamin C derivatives, technical support, and actives expertise helps you select the right derivative and build formulations that are both high-performing and commercially robust.
Vitamin C remains a cornerstone ingredient in skincare. It brightens the complexion, protects against free radicals, and boosts collagen production.1,2 However, pure L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA) is notoriously unstable—leading to shorter shelf lives, formulation difficulties, and potential skin irritation.2,5 For formulators, selecting the ideal derivative is crucial to harnessing Vitamin C’s full potential.
This guide examines four widely used water-soluble Vitamin C derivatives1,2,5—L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA), Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP), Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP), and Ascorbyl Glucoside (AG). We compare these compounds based on stability, pH compatibility, solubility, and efficacy. Whether you are designing a high-impact serum or a gentle daily moisturizer, these insights enable you to formulate with confidence while remaining accessible to less experienced innovators.
Key Criteria for Choosing a Vitamin C Derivative
Selecting the optimal Vitamin C derivative involves several critical factors. Each criterion plays a unique role in supporting product performance and skin compatibility.
Stability and Longevity
While L-Ascorbic Acid is potent, it degrades rapidly when exposed to air, light, or water.2,5 In contrast, stabilized derivatives—such as SAP, MAP, and AG—offer an extended shelf life while maintaining beneficial properties.2,5,6–8 Here, “stability” refers to an ingredient’s ability to retain its effectiveness over time against environmental stressors. Manufacturers dedicate extensive efforts to optimizing formulations for strong resilience.
pH Compatibility
The performance of Vitamin C derivatives depends on the formulation’s pH:
- Topical L-ascorbic acid is most effectively absorbed when formulated at an acidic pH below about 3.5, but these low-pH formulations can cause stinging, erythema, or dryness in sensitive skin.3,4
- SAP and MAP operate best at a near-neutral pH (5.0–7.0), offering greater formulation flexibility and gentler skin tolerance.5–7
Adjusting the pH not only influences ingredient performance but also impacts the overall sensory experience of the final product.
Solubility
All four derivatives are water-soluble, making them ideal for serums, toners, and other aqueous formulas. Water solubility affects product texture, absorption, and consistency. It also facilitates the smooth integration of additional hydrophilic ingredients, ensuring uniform application and easier manufacturing.
Efficacy and Tolerability
L-Ascorbic Acid offers rapid and potent results due to its high bioavailability and direct antioxidant action.1,2 However, its potency and low-pH requirements can contribute to irritation, particularly at higher levels. In contrast, SAP, MAP, and AG require enzymatic conversion on the skin—a process that gradually releases active Vitamin C and enhances tolerability.2,6–8 While L-AA may deliver immediate impact, the stabilized derivatives provide sustained benefits with a lower risk of adverse reactions.
At-a-Glance: Technical Comparison of Vitamin C Derivatives
Below is a table summarizing the critical features of each derivative:
| Vitamin C Derivative | Optimal pH Range | Stability Level | Recommended Concentration | Key Benefits | Ideal Applications |
| L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA) | 3.0–3.5 | Moderate to Low | 10–20%2,3 | Rapid brightening; direct antioxidant action; collagen boost | High-impact serums; targeted treatments |
| Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP) | 5.5–7.0 | High | 1–5%7 | Gentle; supports acne care; versatile pH range | Daily serums; toners; lightweight moisturizers |
| Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP) | 5.0–7.0 | High | 3–10%6 | Brightening; collagen support; anti-aging benefits | Creams; lotions; emulsions |
| Ascorbyl Glucoside (AG) | 5.0–7.0 | High | 2–10%2,8 | Stable; gradual release; highly tolerable | Daily serums; light lotions; “clean” skincare |
Deep Dive into the Main Derivatives
With the core selection criteria in mind, the next step is choosing the right Vitamin C derivative for your specific formulation. Below, we break down the advantages, challenges, and ideal use cases for L-Ascorbic Acid, Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate, Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate, and Ascorbyl Glucoside.
The Benchmark: Pure L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA)
L-Ascorbic Acid is widely recognized as the “gold standard” in Vitamin C skincare.1,2 Its key characteristics include:
Advantages
- Direct Potency: L-AA supplies readily bioavailable Vitamin C that brightens skin, provides antioxidant protection, and supports collagen production.1,2
- Clinically Proven: Concentrations of 10–20% have shown significant improvements in skin tone and texture while reducing photodamage.2,3
Challenges
- Oxidation Sensitivity: Exposure to air, light, or water causes rapid degradation, leading to loss of potency and color changes.2,5
- Low pH Requirement: The acidic environment (pH ~3.0–3.5) necessary for L-AA can be problematic for sensitive skin and requires careful process control.3,4
- Specialized Packaging: L-AA formulations often require airtight, opaque packaging to limit degradation, which can elevate production costs and complexity.2,5
Ideal Use
L-Ascorbic Acid is best suited for high-impact serums or targeted treatments designed for experienced users seeking immediate, visible results.
The Stable Workhorses: SAP and MAP
Both Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP) and Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP) are favored for their enhanced stability and formulation versatility.
Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP)
- Works best at a pH of approximately 5.5–7.0.5,7
- Acts as an antioxidant and has reported antibacterial properties, making it attractive for acne-prone formulations.7
- Gentle on the skin and suitable for sensitive formulas.
- Typically used at 1–5% concentrations; results appear gradually due to its need for enzymatic conversion at the skin surface.7
SAP is optimal for daily serums, toners, and products targeting acne-prone or combination skin without driving excessive irritation.7
Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP)
- Supports collagen synthesis and improves skin brightness by inhibiting melanogenesis.2,6
- Performs optimally at a pH of 5.0–7.0, aligning well with most emulsion systems.5,6
- Commonly incorporated at concentrations of 3–10% to deliver gradual, sustained benefits.6
MAP is especially suited for creams, lotions, and oil-in-water emulsions aimed at anti-aging benefits, dark spot reduction, and long-term tone evenness.
Together, SAP and MAP lower the risk of irritation while offering excellent compatibility with complementary actives such as niacinamide, panthenol, and ceramides.2,6,7
The Gentle Performer: Ascorbyl Glucoside (AG)
Ascorbyl Glucoside (AG) stands out for its exceptional stability and mild profile:
- Outstanding Stability: AG remains stable for extended periods, even in the presence of water, air, and light relative to pure ascorbic acid.2,5,8
- Gradual Activation: After application, AG is slowly converted into active Vitamin C by skin enzymes, facilitating sustained delivery.2,8
- Enhanced Tolerability: AG is ideal for sensitive or reactive skin, though its effects may develop more gradually compared to L-AA. Recommended usage often ranges from 2–10%.2,8
AG is best used in daily serums, light lotions, and “clean” beauty concepts where long-term skin health and visible radiance are prioritized over intense, short-term activity.
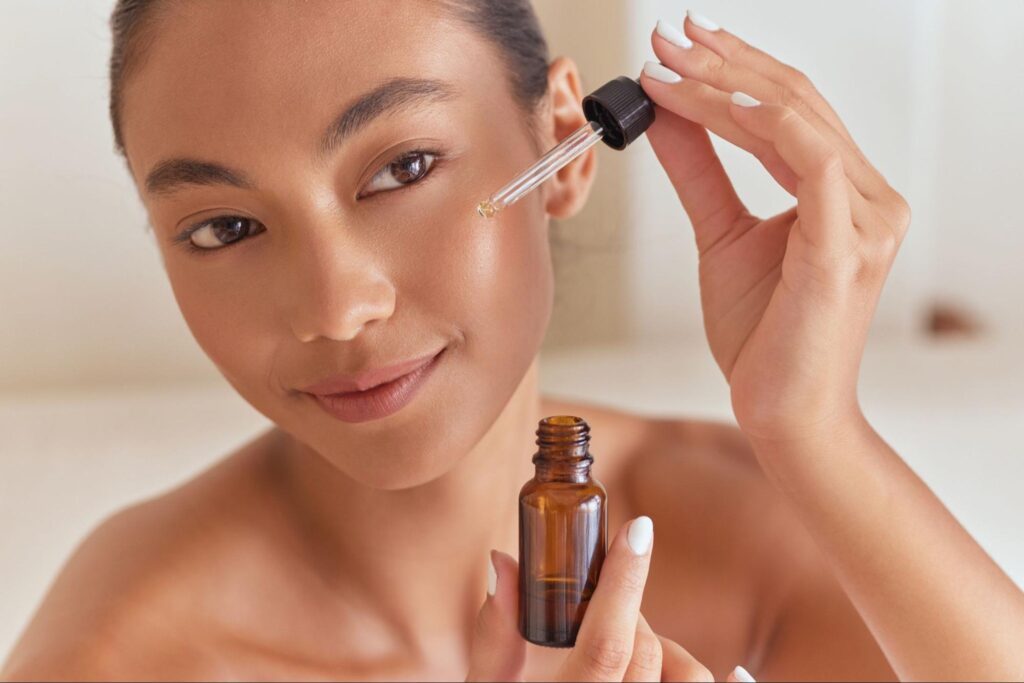

How to Choose the Best Vitamin C Derivative for Your Formula
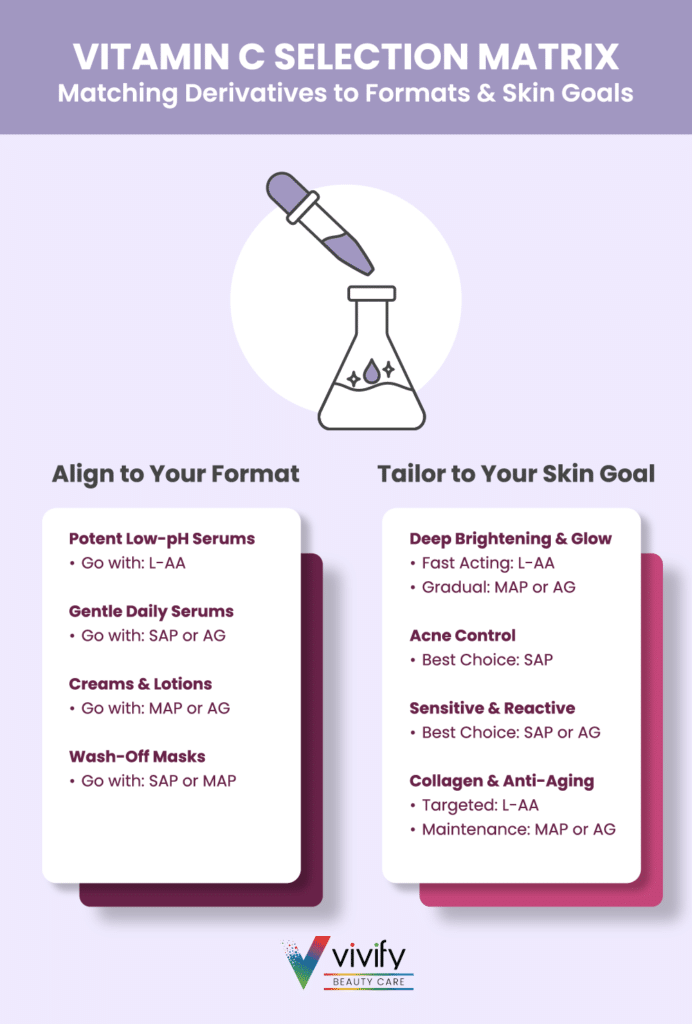
Selecting the right Vitamin C derivative starts with two key decisions: what format you’re creating and which skin concern you’re targeting. Use the guidelines below as a quick decision framework to narrow in on the most suitable option.
Choose by Product Format
Serums (water-based, lightweight, high-impact)
- L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA)
- Best for: High-performance, fast-acting brightening/anti-aging serums.1–3
- Use when: You can formulate at low pH (~3.0–3.5), support the system with synergistic antioxidants, and invest in protective packaging.
- SAP or AG
- Best for: Daily, gentle serums and sensitive- or acne-prone-skin products.2,7,8
- Use when: You want higher stability, better tolerability at near-neutral pH, and a smoother development path.
Creams & Lotions (emulsions, hydrating systems)
- MAP or AG
- Best for: Leave-on moisturizers with anti-aging and brightening claims.2,6,8
- Use when: You’re formulating oil-in-water emulsions at pH ~5.0–7.0 and want sustained, long-term benefits without strong irritation potential.
Masks & Wash-Off Treatments (short-contact, intensive)
- SAP or MAP
- Best for: Rinse-off masks, peels, and boosters where higher active levels can be used for a short exposure.6,7
- Use when: You want noticeable radiance and texture benefits without relying on long-term wear, and can support with other exfoliating or brightening actives.
Choose by Skin Concern
Hyperpigmentation & Uneven Tone
- Primary options: L-AA, MAP, AG.2,3,6,8
- L-AA for maximum, fast brightening in robust, low-pH serums.
- MAP or AG for more stable, gradual brightening in daily-use products and creams.
Acne-Prone & Blemish-Prone Skin
- Primary option: SAP.7
- Leverage SAP’s antioxidant and reported antibacterial benefits in lightweight serums or toners at near-neutral pH.
- Pair with niacinamide or gentle exfoliants for a comprehensive anti-blemish system.
Sensitive or Reactive Skin
- Primary options: SAP, AG.2,7,8
- Prioritize high-stability, gradual-release derivatives at pH ~5.5–7.0.
- Avoid very low pH and high L-AA percentages; combine with soothing agents such as panthenol, allantoin, or barrier-supporting botanicals.
Mature, Photo-Damaged, or Dry Skin
- Primary options: L-AA, MAP, AG.1–3,6,8
- L-AA in targeted serums for strong collagen support and brightening where tolerability allows.
- MAP or AG in richer creams/lotions with lipids, ceramides, and peptides to support barrier repair and long-term firmness.

Formulation Strategies to Maximize Stability & Efficacy
Once you’ve selected the right Vitamin C derivative, smart formulation choices will strongly influence performance over the product’s lifetime. The strategies below help protect your active, optimize delivery, and support consistent in-market results.
pH Control
pH strongly influences both Vitamin C stability and skin compatibility.3–7
- L-Ascorbic Acid (L-AA) performs best at a low pH (~3.0–3.5), but this can be more irritating and must be tightly controlled during scale-up.3,4
- SAP, MAP, and AG are more forgiving, functioning well at near-neutral pH (~5.0–7.0), which simplifies emulsification and improves tolerability.5–8
- Regular pH checks throughout development and production—especially after heating, emulsification, and cooling—are essential to maintain performance.
Packaging & Antioxidant Synergy
Oxidation is a primary cause of Vitamin C degradation, so both packaging and formula design should work together to protect the active.2,5
- Use airless pumps, opaque or amber containers, and minimal headspace to reduce exposure to oxygen and light.
- Combine Vitamin C with supporting antioxidants (e.g., Vitamin E, ferulic acid) and chelating agents to slow oxidation and extend shelf life.2
- Thoughtful packaging, paired with a well-built antioxidant network, can meaningfully support product potency under real-world storage conditions.
For additional antioxidant options, you can explore antioxidant actives in the Vivify portfolio.
Encapsulation & Delivery Systems
Encapsulation technologies can improve both stability and skin delivery, particularly for more oxidation-prone or high-value formulas.9
- Liposomes, microcapsules, and polymer-based systems create a protective barrier around Vitamin C, limiting premature degradation.
- Controlled-release systems allow for gradual delivery, which can reduce irritation and enhance bioavailability over time.9
- Choosing the right delivery system depends on your derivative, product format, and desired claim (e.g., “time-release brightening serum,” “advanced encapsulated Vitamin C”).
Vivify also offers specialized delivery systems such as active-loaded granules that can complement Vitamin C-focused formulas.
Testing & Quality Control
Robust testing confirms that your chosen strategy performs over the product lifecycle.2,5,9
- Conduct stability studies (accelerated and real-time) under varied temperature, humidity, and light conditions to track potency, color, odor, and pH.
- Use laboratory assays (e.g., active content, antioxidant capacity) and, where appropriate, clinical or instrumental evaluations to validate claims such as brightening or wrinkle reduction.
- Implement ongoing in-process and finished-goods QC to help each batch match your validated profile, from lab to full-scale manufacturing.
Together, these strategies support consistent, evidence-backed results—strengthening both consumer satisfaction and long-term brand credibility.
Integration with Complementary Actives
Formulators are increasingly exploring how Vitamin C derivatives work in synergy with other active ingredients. Combining Vitamin C with peptides, hyaluronic acid, and retinol can enhance skin rejuvenation and hydration.1,2 For instance, peptides combined with stabilized Vitamin C derivatives may further support collagen production, creating a multi-dimensional anti-aging effect. Likewise, adding hyaluronic acid supports moisture retention and may assist in delivering Vitamin C deeper into the skin layers.
This integrated approach helps ensure that each product benefits from a well-rounded formulation optimized for both immediate and long-term results.
Regulatory, Quality, and Commercialization Essentials

Bringing a Vitamin C formula from lab to launch requires more than strong performance—it must also align with regulatory expectations and be reliably reproducible at scale.
Compliance & Safety
- Align formulas with regional cosmetic regulations (e.g., US, EU, other target markets).
- Complete safety assessments, ingredient reviews, and appropriate labeling for claims and usage directions.
Technical Documentation
- Maintain up-to-date TDS, SDS, CoAs, and specifications for all Vitamin C derivatives and key raw materials.
- Document stability data, preservative efficacy, and claim substantiation to support audits, customer inquiries, and distributor requirements.
Partnering with Reputable Suppliers
- Work with suppliers who provide robust technical support, regulatory guidance, and consistent quality from batch to batch.
- Look for partners that can offer sample formulations, troubleshooting assistance, and regulatory-ready documentation, helping shorten development timelines and de-risk commercialization.
With strong compliance, clear documentation, and trusted supply partners, formulators can confidently scale Vitamin C innovations from the bench to the marketplace.
Emerging Innovations & Sustainable Vitamin C Formulations
Innovation in Vitamin C delivery is increasingly focused on better performance with a lighter environmental footprint.1,2,9
- Nanoscale Systems: Nanoemulsions and other nanoscale carriers help protect Vitamin C from oxidation and can improve its delivery to the skin.9
- Hybrid Encapsulation: Combining different encapsulation methods supports both stability on the shelf and controlled release on the skin.
- Eco-Friendly Stabilizers: Formulators are increasingly using more naturally derived antioxidants and chelators to stabilize Vitamin C while supporting “clean” positioning.
- Biodegradable Systems: New carrier systems are being designed with biodegradable materials, helping reduce long-term environmental impact.9
These advances allow brands to offer Vitamin C formulas that are both high-performing and aligned with the growing demand for sustainable innovation.
Selecting the Optimal Vitamin C Derivative
Choosing the right Vitamin C derivative is critical to balancing potency, stability, and tolerability. L-Ascorbic Acid offers powerful, immediate effects, while SAP, MAP, and AG provide enhanced stability and gentler performance. Your choice should align with the intended application, target skin functions, and formulation constraints.
By controlling pH levels, employing innovative packaging, leveraging antioxidant synergy, utilizing advanced delivery systems, and conducting rigorous testing, formulators can design products that consistently deliver exceptional results.1–9 Embracing emerging trends and adhering to strict regulatory standards will support the long-term success of your skincare formulations.
At Vivify Beauty Care, our robust portfolio of high-performance ingredients and technical expertise is here to help you overcome formulation challenges. Explore our range of Vitamin C derivatives and related actives and take the next step in realizing your skincare innovation. Contact us today for more in-depth details on our actives.
References
- Pullar, J. M., Carr, A. C., & Vissers, M. C. M. (2017). The roles of vitamin C in skin health. Nutrients, 9(8), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9080866 (Formula Botanica)
- Al-Niaimi, F., & Chiang, N. Y. Z. (2017). Topical vitamin C and the skin: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 10(7), 14–17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5605218/ (Lippincott Journals)
- Pinnell, S. R., Yang, H., Omar, M., Riviere, N. M., DeBuys, H. V., Walker, L. C., Wang, Y., & Levine, M. (2001). Topical L-ascorbic acid: Percutaneous absorption studies. Dermatologic Surgery, 27(2), 137–142. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042728-200102000-00008 (PubMed)
- Telang, P. S. (2013). Vitamin C in dermatology. Indian Dermatology Online Journal, 4(2), 143–146. https://doi.org/10.4103/2229-5178.110593 (Vivify Beauty Care)
- Segall, A. I., & Moyano, M. A. (2008). Stability of vitamin C derivatives in topical formulations containing lipoic acid, vitamins A and E. International Journal of Cosmetic Science, 30(6), 453–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2494.2008.00473.x (youtube.com)
- Kameyama, K., Sakai, C., Kondoh, S., Yonemoto, K., Nishiyama, S., Tagawa, M., Murata, T., Ohnuma, T., Quigley, J., Tadokoro, T., & Hidehisa, S. (1996). Inhibitory effect of magnesium L-ascorbyl-2-phosphate (VC-PMG), a stable vitamin C derivative, on melanogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 34(1), 29–33. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8543691/ (L’Oréal Dermatological Beauty)
- Woolery-Lloyd, H., Baumann, L., & Ikeno, H. (2010). Sodium L-ascorbyl-2-phosphate 5% lotion for the treatment of acne vulgaris: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 9(1), 22–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1473-2165.2010.00480.x (PubMed)
- Takada, M., Numano, K., Nakano, M., Yamamoto, A., & Imokawa, G. (2024). Treatment with ascorbyl glucoside–arginine complex ameliorates solar lentigos. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(24), 13453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms252413453 (Tojo Cosmetics)
- Miah, M. S., Rahman Chy, M. W., Ahmed, T., Suchi, M., Muhtady, M. A., Ahmad, S. N. U., & Hossain, M. A. (2025). Emerging trends in nanotechnologies for vitamin delivery: Innovation and future prospects. Nano Trends, 10, 100126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nwnano.2025.100126 (Vivify Beauty Care)
Disclaimer
The information provided in this blog is intended for general informational purposes only and is furnished without warranty, expressed or implied. The content reflects insights and information accurate to the best knowledge of Vivify Beauty Care at the time of publication.
This blog content should be used as a general guide and does not constitute a substitute for direct professional advice or product-specific consultation. Vivify Beauty Care does not validate any claims made within the blog, and customers bear the ultimate responsibility for ensuring their product applications and associated claims are compliant with all applicable laws and regulations. For specific inquiries or tailored recommendations regarding our product specifications and service offerings, please contact our sales professionals.



